
Ten Pyrex tubes (25 x 600 mm) were each filled with 20.0 g. (0.253 mole) of selenium and 100 g. of alumina pellets (Fluka 1—3 mm). The tubes had been cleaned with hot concentrated nitric acid, water and finally preheated empty but with a slow stream of nitrogen in the tube oven at 450° for 2 hours. The filled tubes were subsequently placed in the oven, and a slow stream of nitrogen was passed through the tubes until the temperature was 450°. Then the nitrogen was replaced by acetylene, and after some minutes a flashing occurred, which deposited a carbonaceous material in the tubes. If flashing does not occur spontaneously, the introduction of some air into the tubes will help. This is done by removing the gas inlet joints at each tube (one at a time) for one second. A brown crude oil begins to form, and after 7-8 hours the formation of the oil subsides, and it is not worthwhile to continue the reaction. The crude product is collected from several runs and distilled.
After cooling, the tubes are emptied of alumina pellets, which are used again together with a new portion of 200 g. of selenium.
The reaction becomes more efficient after 5—6 runs, and the same catalyst (alumina covered with a black material formed in the reaction) could be used 25 times without any significant drop in yield.
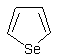
The crude product is distilled, b.p. 105—120°, to give 95% pure selenophene, which is sufficiently pure for most synthetic purposes.
The catalyst becomes very inefficient when stored in a hood in which a cleaning bath with concentrated nitric acid is placed. Similarly, the outlet gas stream from the reaction tubes, which certainly contains hydrogen selenide, deactivates the catalyst at ordinary temperatures. The yield of selenophene dropped to less than 5% when the catalyst was stored in the same hood as the tube oven.
© Collected Ruslan Anatolievich Kiper, burewestnik@mail.ru